xdialog: A simple and beautiful JavaScript dialog library
xdialog is a simple JavaScript library to create beautiful modern dialogs with lots of cool effects using CSS3 transitions and transforms.
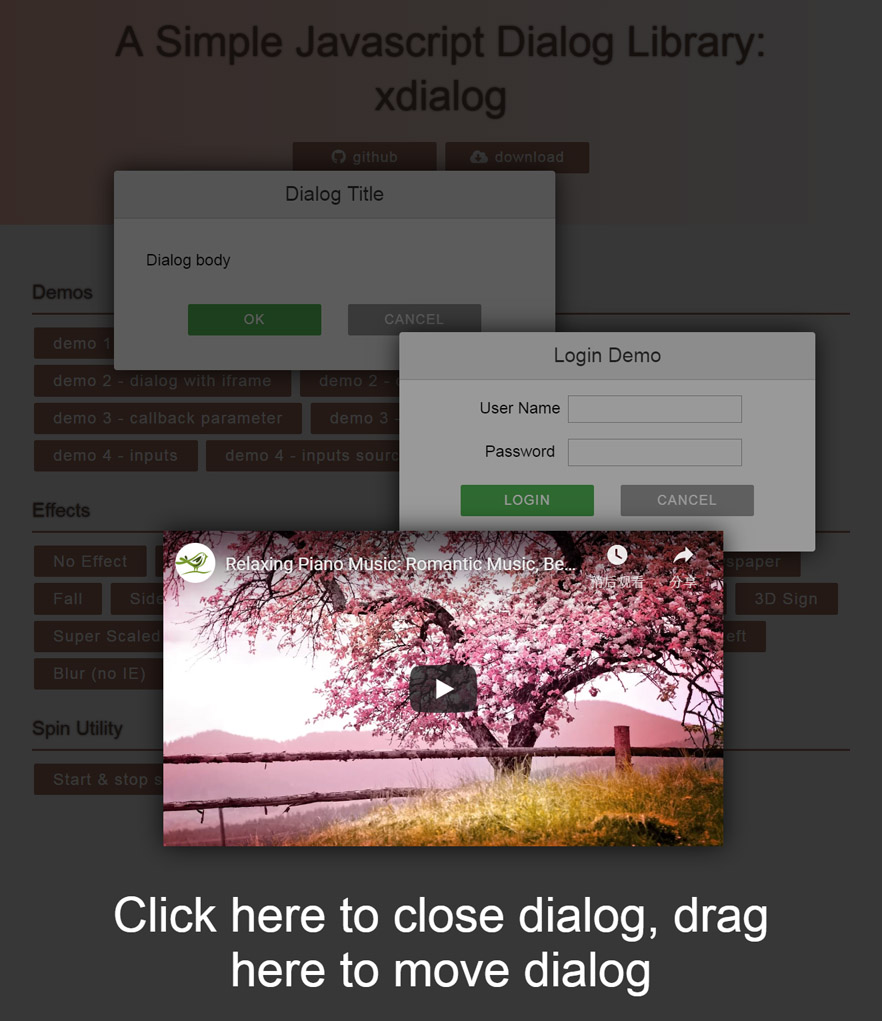
Online demo is here xdialog demo
Main features of xdialog
- Using vanilla JavaScript and CSS
- No dependency
- Modern and beautiful default UI
- Simple usage
- Lots of cool open/close effects
- Lots of options and callbacks can be used to customize easily
- Enter key to ok
- ESC key to cancel
- Click overlay to cancel
- Drag dialog/overlay to move dialog
- Supports iframe content such as YouTube videos
Background
Inspired by codrops’ ModalWindowEffects, this dialog library enhanced some of the original CSS effects, and added many convenient functions.
Installation
You can use CDN or local method to install.
-
CDN
Insert the following code into your html file.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xxjapp/xdialog@3/xdialog.min.css"> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xxjapp/xdialog@3/xdialog.min.js"></script>Or for non-min version, use this.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xxjapp/xdialog@3/xdialog.css"> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/xxjapp/xdialog@3/xdialog.js"></script>Thanks to jsdelivr, jsdelivr CDN works like magic. For more details, please refer https://www.jsdelivr.com/package/gh/xxjapp/xdialog.
-
Local
- Download xdialog library file xdialog.x.y.z.min.zip or xdialog.x.y.z.zip from release page and unzip it.
- Insert the Stylesheet xdialog.min.css and JavaScript xdialog.min.js into the html file.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="path/to/xdialog.min.css"> <script src="path/to/xdialog.min.js"></script>Or insert non-min version files if you like.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="path/to/xdialog.css"> <script src="path/to/xdialog.js"></script>
Usage
Just call xdialog API to open or create dialogs, like the following. See Reference for more details.
let dialog1 = xdialog.open(); // open is a shortcut of create + show
dialog1.close(); // close is a shortcut of hide + destroy
let dialog2 = xdialog.create({title: 'Hello, xdialog', body: 'This is a message.'});
dialog2.show();
dialog2.hide();
dialog2.destroy();
Reference
xdialog API
xdialog methods
-
xdialog.init(options)
initialize xdialog options.zIndex0 - initial z index to use, default value is 10000 -
xdialog.create(options)
create a dialogSEE: default options
-
xdialog.open(options)
create a dialog and show itSEE: default options
-
xdialog.alert(text, options)
display an alert dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.confirm(text, onyes, options)
display a confirm dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.info(text, options)
display an information dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.warn(text, options)
display a warning dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.error(text, options)
display an error dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.fatal(text, options)
display a fatal error dialog, please view the source for details -
xdialog.dialogs()
get all dialog instances
xdialog utility methods
-
xdialog.startSpin()
start spin animation -
xdialog.stopSpin()
stop spin animation
dialog API
dialog attributes
-
dialog.id
dialog html element id -
dialog.element
dialog html element
dialog methods
-
dialog.show()
show dialog -
dialog.hide()
hide dialog -
dialog.destroy()
destroy dialog -
dialog.close()
hide dialog and destroy it -
dialog.adjust()
adjust dialog to make the whole dialog visible -
dialog.fixChromeBlur()
fix chrome blur
default options
Default options will be used if you create / open dialog without corresponding attributes. You can overwrite these with your own values.
{
// dialog title
// use null value to remove title
title: 'Dialog Title',
// dialog body
//
// valid values:
// - null
// no body
//
// - string
// body html
//
// - object
// src: body source selector
// element: body source dom element
//
// please use element when selector not usable
//
// example:
// {
// src: '#demo6-content'
// element: document.getElementById('demo6-content')
// }
body: '<p>Dialog body</p>',
// dialog buttons
//
// valid values:
// - null
// no buttons
//
// - array
// predefined button name or user defined button html like
// example: ['ok', 'cancel', 'delete', '<button id="my-button-id" class="my-button-class">Button-text</button>']
//
// - object
// button name to button text(predefined) or button html(user defined) or attribute object map like
// example: {
// ok: {
// text: 'okay',
// style: 'background:#4336f4;',
// clazz: 'xd-button xd-ok demo-copy-button'
// },
// delete: 'Delete',
// cancel: 'Cancel',
// other: '<button id="my-button-id" class="my-button-class">Button-text</button>'
// }
buttons: ['ok', 'cancel'],
// dialog extra classes
// for example 'xd-fatal my-dialog-class'
extraClass: '',
// dialog extra style
// for example 'width: 640px;'
style: '',
// dialog show/hide effect, one of the following values
// - fade_in_and_scale
// - slide_in_right
// - slide_in_bottom
// - newspaper
// - fall
// - side_fall
// - sticky_up
// - 3d_flip_horizontal
// - 3d_flip_vertical
// - 3d_sign
// - super_scaled
// - just_me
// - 3d_slit
// - 3d_rotate_bottom
// - 3d_rotate_in_left
// - blur
// - let_me_in
// - make_way
// - slip_from_top
//
// use '' or null value to disable effect
effect: 'fade_in_and_scale',
// fix dialog blur for chrome browser with/without transform and/or with/without perspective
//
// true: to fix
// false: not to fix
//
fixChromeBlur: true,
// modal or not
modal: true,
// timeout in seconds to close dialog automatically
// use 0 value to disable closing dialog automatically
timeout: 0,
// listen enter key press or not
listenEnterKey: true,
// listen ESC key press or not
listenESCKey: true,
// callback when dialog element is about to be created
// return false to stop creating process
beforecreate: null,
// callback when dialog element has been created
aftercreate: null,
// callback before show
// return false to stop showing process
beforeshow: null,
// callback after show
aftershow: null,
// callback before hide
// return false to stop hidding process
beforehide: null,
// callback after hide
afterhide: null,
// callback when OK button pressed
// return false to avoid to be closed
onok: null,
// callback when Cancel button pressed
// return false to avoid to be closed
oncancel: null,
// callback when Delete button pressed
// return false to avoid to be closed
ondelete: null,
// callback when dialog is about to be destroyed
// return false to avoid to be destroyed
ondestroy: null,
// callback when drag will start
// return false to avoid being dragged by default process
// return true to allow being dragged
// otherwise to go default process
ondrag: null,
}
callback function format
default
All callback functions use the same prototype, except the ones with special instruction.
/**
* @param {Object} param - callback parameter
* @param {String} param.id - dialog html element id
* @param {Element} param.element - dialog html element
* @param {Object} param.dialog - dialog instance
* @param {Element} param.overlay - dialog overlay element
* @param {Event} param.event - event if any
*/
function callback(param)
callback for ondrag
/**
* @param {Element} element - element clicked
* @param {Element} destElement - element to be moved
* @param {Element} srcElement - element to drag on
*/
function ondrag(element, destElement, srcElement)
Example: let jquery Sortable to handle some element’s dragging.
SEE: https://jqueryui.com/sortable/
ondrag: function(element) {
if ($(element).closest('.ui-sortable').length > 0) {
return false;
}
// otherwise let go default process
}